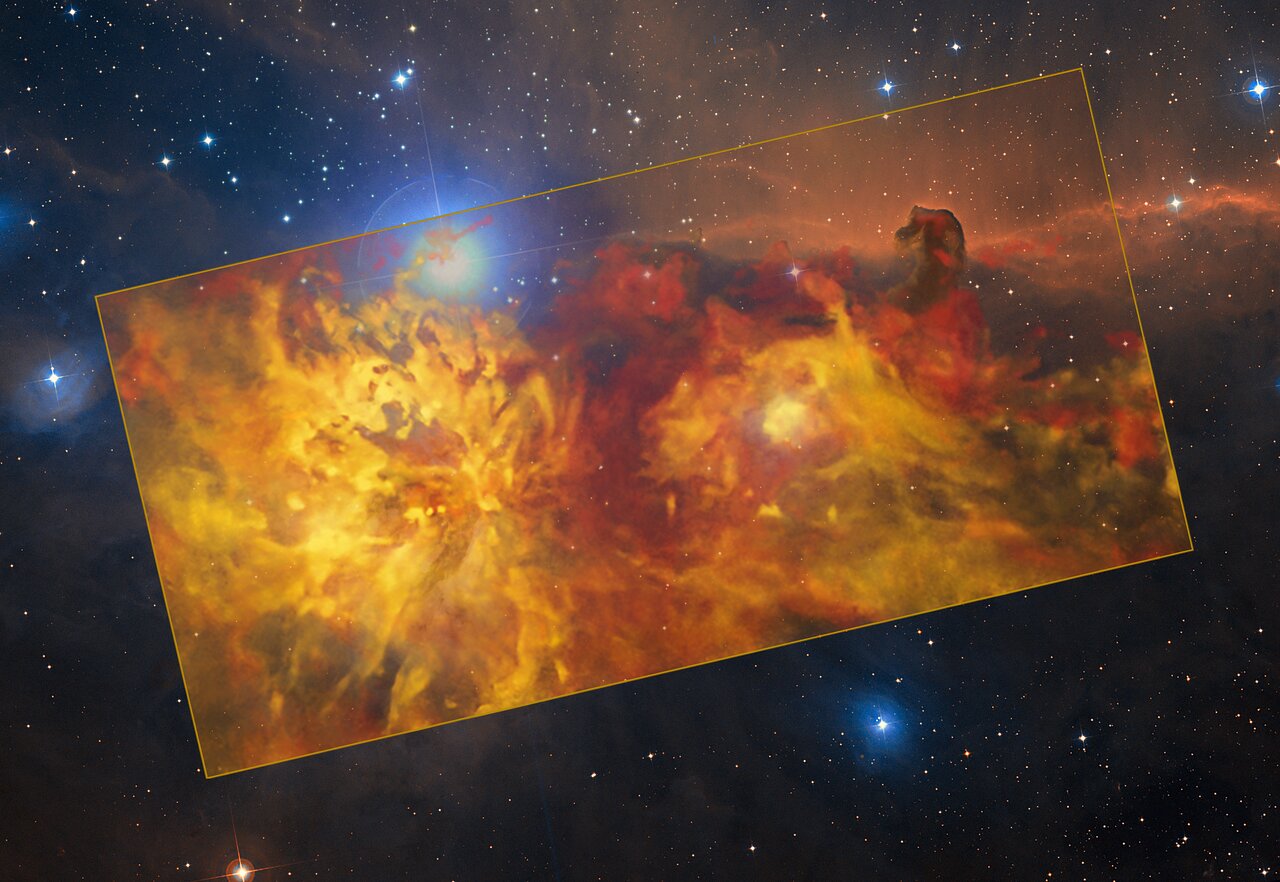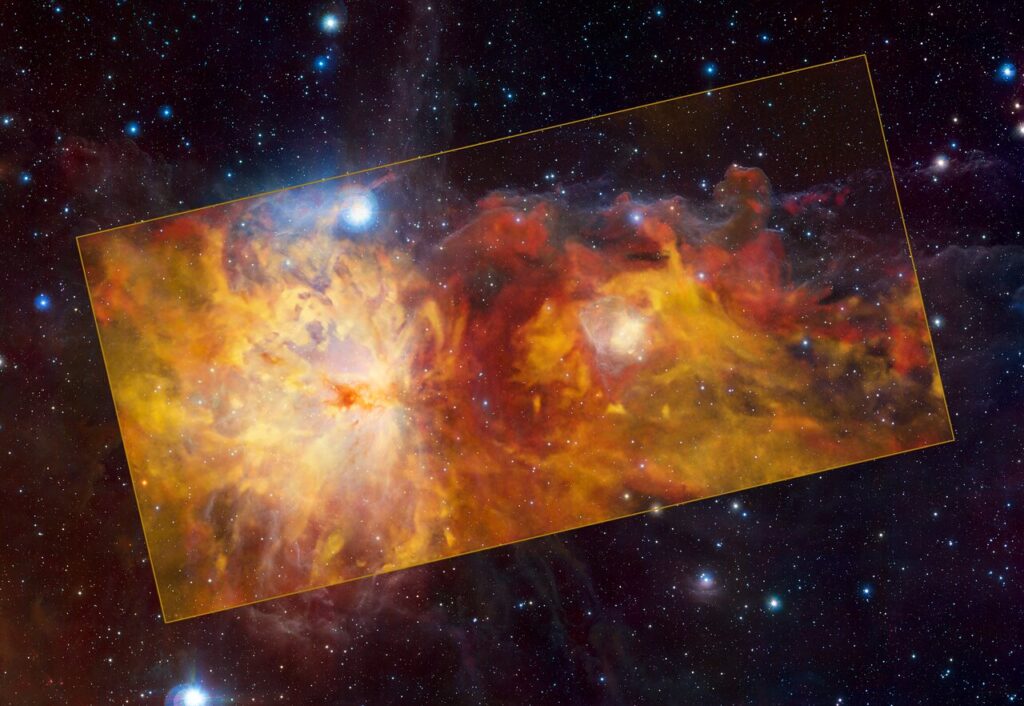
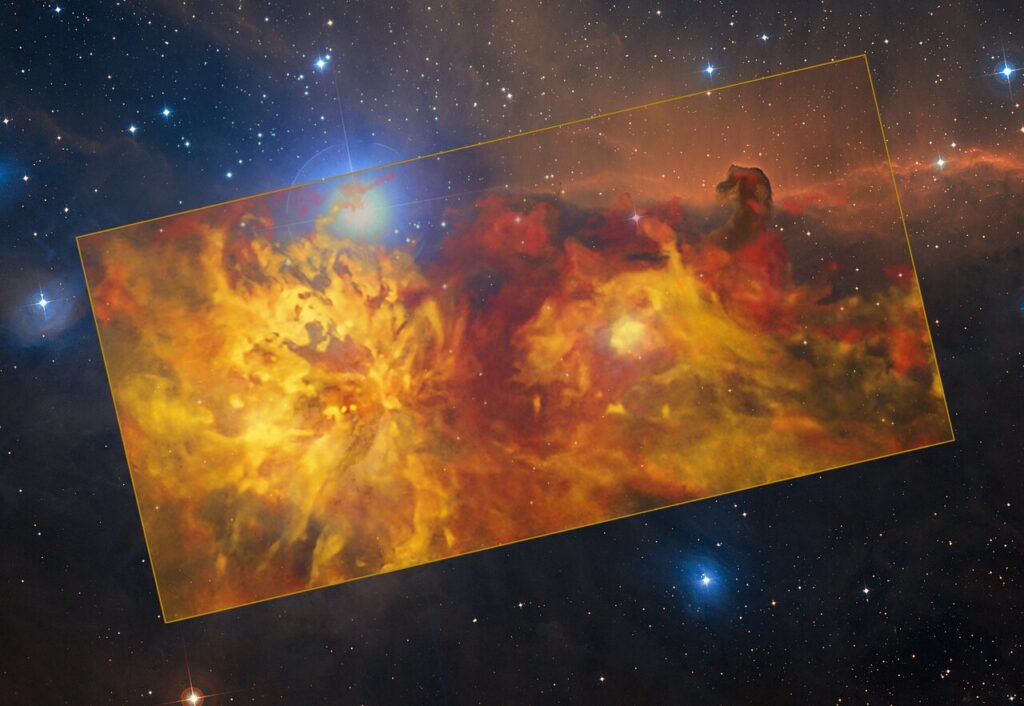
There’s an adage in astronomy about how there’s always something new to find in the constellation of Orion—well, astronomers just found his fireplace.
In a new series of images, the aptly-named “Flame Nebula” located in Orion appears like a raging inferno, as radiation released by young stars causes clouds of gases and dust to glow.
The spectacular image was snapped by the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment at the European Southern Observatory in Chile’s Atacama Desert, the perfect place for professional stargazing due to it being very far from any light pollution and located at a very high altitude.
It’s a composite image, with instruments that view in radio waves providing the blazing oranges, and a second infrared spectrum telescope providing the precise background.
Optical light can’t make it through the dense nebulae, but infrared light can, so using both allows scientists to have an unobstructed view.
Orion is one of the most famous regions in the sky, and the image contains the iconic Horsehead Nebula in the top right in addition to the Flame Nebula. The lighter colored swirl in the middle-right is the reflection of another nebula NGC 2023. The team even discovered one new nebula, a small object, remarkable because of its almost perfectly circular appearance, which they named the Cow Nebula.
RELATED: Huge Supply of Water Discovered on Mars, Frozen at the Bottom of its Grand Canyon
“As astronomers like to say, whenever there is a new telescope or instrument around, observe Orion: there will always be something new and interesting to discover!” ESO Thomas Stanke said in a statement.

Nebulae are often referred to as cosmic nurseries, and are areas in which clouds of gases and dust coalesce into stars. This makes them extremely photogenic places, and the clouds in the image are known as the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex.
Located between 1,300 and 1,600 light-years away from Earth, they contain the most active stellar nursery in the Solar System’s neighborhood.
Unlike what the “fire” of this image might suggest, these clouds are actually cold, with temperatures typically just a few tens of degrees above absolute zero.
MORE: Astronomers Capture Black Hole Eruption Spanning 16 Times the Full Moon in the Sky
“The different colors indicate the velocity of the gas,” ESO officials wrote in the statement. “The Flame Nebula and its surroundings are moving away from us, with the red clouds in the background receding faster than the yellow ones in the foreground.”
WATCH ESO stack their images atop one another in the video below.
SHARE These Far Out Photos With More Cosmic Fans…




















