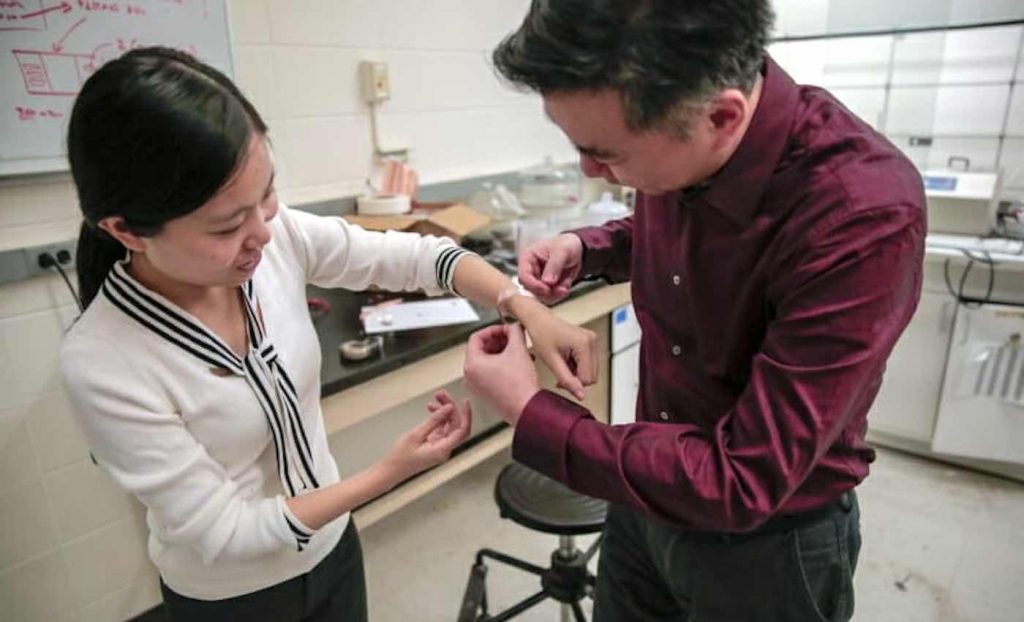
Engineers have developed a new, low-cost bandage that speeds up healing times from nearly two weeks to just three days.
The method, which was developed by researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, leverages energy generated from a patient’s own body motions to apply gentle electrical pulses at the site of an injury.
“We were surprised to see such a fast recovery rate,” says Xudong Wang, a professor of materials science and engineering at UW-Madison. “We suspected that the devices would produce some effect, but the magnitude was much more than we expected.”
Wang and collaborators described their wound dressing method in the journal ACS Nano.
Researchers have known for several decades that electricity can be beneficial for skin healing, but most electrotherapy units in use today require bulky electrical equipment and complicated wiring to deliver powerful jolts of electricity.
“Acute and chronic wounds represent a substantial burden in healthcare worldwide,” says collaborator Angela Gibson, professor of surgery at UW-Madison and a burn surgeon and director of wound healing services at UW Health. “The use of electrical stimulation in wound healing is uncommon.”
In contrast with existing methods, the new dressing is much more straightforward.
“Our device is as convenient as a bandage you put on your skin,” says Wang.
The new dressings consist of small electrodes for the injury site that are linked to a band holding energy-harvesting units called nanogenerators, which are looped around a wearer’s torso. The natural expansion and contraction of the wearer’s ribcage during breathing powers the nanogenerators, which deliver low-intensity electric pulses.
“The nature of these electrical pulses is similar to the way the body generates an internal electric field,” says Wang.
CHECK OUT: New Peanut Allergy Drug Shows Life-Saving Potential – and It Could Be Available as Soon as 2019
And, those low-power pulses won’t harm healthy tissue like traditional, high-power electrotherapy devices might.
In fact, the researchers showed that exposing cells to high-energy electrical pulses caused them to produce almost five times more reactive oxygen species – major risk factors for cancer and cellular aging – than cells that were exposed to the nanogenerators.
Also a boon to healing: They determined that the low-power pulses boosted viability for a type of skin cell called fibroblasts, and exposure to the nanogenerator’s pulses encouraged fibroblasts to line up (a crucial step in wound healing) and produce more biochemical substances that promote tissue growth.
“These findings are very exciting,” says collaborator Weibo Cai, a professor of radiology at UW-Madison. “The detailed mechanisms will still need to be elucidated in future work.”
In that vein, the researchers aim to tease out precisely how the gentle pulses aid in healing. Additionally, they are working to give the nanogenerators additional capabilities – tweaking their structure to allow for energy harvesting from small imperceptible twitches in the skin or the thrumming pulse of a heartbeat.
“The impressive results in this study represent an exciting new spin on electrical stimulation for many different wound types, given the simplicity of the design,” says Gibson, who will collaborate with the team to confirm the reproducibility of these results.
MORE: Doctor That Discovered Natural Way to Treat Vertigo for Free Writes Book On How Sufferers Can Thrive
If the team is successful, the devices could help solve a major challenge for modern medicine – and because the nanogenerators consist of relatively common materials, price won’t be an issue.
“We think our nanogenerator could be the most effective electrical stimulation approach for many therapeutic purposes,” says Wang. “I don’t think the cost will be much more than a regular bandage. The device in itself is very simple and convenient to fabricate.”
(Source: University of Wisconsin–Madison)
Help Your Friends Heal From Negativity By Sharing The Good News To Social Media – Photo by Sam Million-Weaver / University of Wisconsin-Madison





















This is fantastic, but I wonder how long it will take to be released to the “common folks” (if ever).
Wasn’t there a guy in the 60’s that invented a device to hold in your hand with a couple of wires hanging out that gave a gentle electric current??? he did this in his garage and was a called a quack???
Well i’m glad they did this anyway. it would help a lot of people and solve alot of problems.